乙型肝炎病毒(Hepatitis B Virus,HBV)感染呈世界范围广泛流行,全球有超过3亿慢性感染者;并逐步发展为慢性乙型肝炎、肝硬化和肝癌,每年约有100万人死于乙肝相关的各种终末期疾病。尽管对HBV感染的控制已越来越引起了人们的重视,不同的方法已运用于控制HBV感染和治疗HBV患者,但治疗HBV患者的两大类药物(核苷酸类似物和干扰素)均不能完全清除人体内的HBV,并且可导致药物抵抗或产生严重的副作用。因此,寻找新的分子生物学治疗靶点,发展新的治疗策略显得尤为重要。
Cyclin D2是细胞周期蛋白家族D的成员之一。在细胞周期进程中,cyclin D2与细胞周期蛋白依赖性激酶4(Cyclin-dependent kinase4,CDK4)和CDK6形成复合物并作为其调节亚基在G1/S转换中发挥了重要作用[1]。有文献报道cyclin D2参与了肿瘤的进展[2],并且在HBV相关的HCC中,cyclin D2的启动子是高度甲基化的[3]。另外,一些细胞周期调节因子如p53、p21也是与HBV相关的HCC的发生发展有关的[4]。这些发现揭示着细胞周期的调节因子与HBV相关的HCC存在某种关联,但目前很少有研究关注于cyclin D2与HBV感染之间的关系。本课题将通过沉默cyclin D2表达和过表达cyclin D2两方面研究cyclin D2是否调控了HBV的复制。
1 材料与方法 1.1 材料HepG2.2.15、HepG2细胞购于ATCC(American Type Culture Collection)公司。包装cyclin D2的shRNA的pLKO.1-puro质粒(产品目录编号 SH2421),包装 scramble shRNA的pLKO.1-puro质粒(产品目录编号 SH2421)均购于Sigma-Aldrich。pcDNA3.1-cyclin D2购于addgene,人乙型肝炎病毒(HBV)复制质粒pGEM-HBV1.3由德国海德堡大学Protzer博士赠送。Cyclin D2抗体(3741)购于Cell Signaling Technology,β-actin抗体(sc-1616-R)购于Santa Cruz Biotechnology。 ELISA试剂盒购于KHB。
1.2 方法 1.2.1 细胞培养和转染方法HepG2细胞培养于含有10%胎牛血清的MEM培养基中,HepG2.2.15培养于含有10%胎牛血清,400 μg/mL G418的MEM培 养基中,在含5% CO2,37 ℃ 孵箱中常规培养。质粒按照Lipofectamin 2 000TM (Invitrogen)的说明书进行转染。
1.2.2 细胞内HBV复制中间体提取和southern blot 分析细胞于六孔板中转染5 d后,去除培养基,PBS清洗,胰酶消化,加入0.5 mL细胞裂解液(10 mmol/L Tris-HCl pH=8.0、1 mmol/L EDTA、1% NP-40和2% sucrose),混匀后,37 ℃ 孵育15 min,转移裂解液到EP管中,15 000×g离心5 min。在上清中加入DNaseⅠ(40 U/mL)和 MgCl2(10 mmol/L),37 ℃孵育≥4 h后加入200 μL 35% PEG 8 000(含1.5 mol/L NaCl),冰 浴1 h后11 000×g、4 ℃离心5 min,留沉淀,加入0.5 mL 蛋白酶K消化液(0.5% SDS,150 mmol/L NaCl,25 mmol/L Tris-HCl pH=8.0和10 mmol/L EDTA)和0.5 mg/mL蛋白酶K(Takara),45 ℃过夜。酚氯仿抽提,异丙醇沉淀,70%乙醇洗涤,TE缓冲液或ddH2O溶解HBV复制中间体。提取的HBV复制中间体经0.9%琼脂糖凝胶电泳,毛细管虹吸法转膜,120 ℃固定。预杂交后加人地高辛标记DNA探针杂交过夜。再化学发光、采集信号。
1.2.3 实时荧光定量PCR(qPCR)提取HBV复制中间体,按照SYBR Green (Roche,Germany)说明书 配制反应体系和设置反应条件,HBV DNA引物,上游:CCTAGTAGTCAGTTATGTCAAC,下游: TCTATAAGC-TGGAGGAGTGCGA。每孔均设3个复孔,每组实验重复3次。
1.2.4 Western blot检测转染3 d后,去除培养基,PBS清洗,RIPA裂解缓冲液裂解细胞,15 min后收集裂解液离心,去除细胞碎片,用BCA法测定蛋白浓度。取等量(30 μg)细胞总蛋白上样,于10%的SDS-PAGE中分离蛋白后,在Bio Rad湿式转移电泳槽转膜。5%脱脂牛奶封闭NC膜1 h,加一抗(1 ∶2 000稀释一抗),4 ℃摇床孵育过夜。然后以TBS-T洗涤3次,每次5 min。二抗(即HRP标记的兔抗人IgG抗体,以封闭液按1 ∶3 000稀释),室温下摇床孵育2 h,洗涤3次后,ECL显影。以β-actin为内参。
1.2.5 HBsAg和HBeAg的检测按照酶联免疫吸附试验(ELISA)试剂盒操作说明检测细胞培养上清中的HBsAg 和 HBeAg的分泌水平。
1.3 统计学处理采用SPSS 17.0软件进行统计,多样本均数间的显著性检验用方差分析,两样本间均数比较采用配对t检验。
2 结果 2.1 细胞周期蛋白家族在HBV复制细胞中的表达水平我们首先验证了细胞周期蛋白家族各成员在HBV复制细胞HepG2.2.15与对照细胞HepG2中的表达差异,qRT-PCR分析发现cyclin D2的mRNA水平在HepG2.2.15细胞中显著高于HepG2细胞(P < 0.01,图1)。
 |
| 1: cyclin A2; 2: cyclin B1; 3: cyclin B2; 4: cyclin C; 5: cyclin D1; 6: cyclin D2; 7: cyclin E1 a:P < 0.05,b:P < 0.01,与HepG2细胞比较图 1 qRT-PCR分析在HepG2.2.15与HepG2细胞中细胞周期家族成员mRNA的表达差异 (n=3,x±s) |
在HepG2细胞中瞬时转染对照质粒pcDNA3.1、HBV表达质粒pCH9/3091和pGEM-HBV1.3后,qRT-PCR检测发现pCH9/3091和pGEM-HBV1.3组中cyclin D2的mRNA水平表达相对值[分别为(2.52±0.35)、(2.3±0.3)]显著高于pcDNA3.1组(1.01±1.01),差异具有统计学意义(P < 0.01)。Western blot检测也发现pCH9/3091和pGEM-HBV1.3能明显增加cyclin D2的蛋白表达水平(图2)。
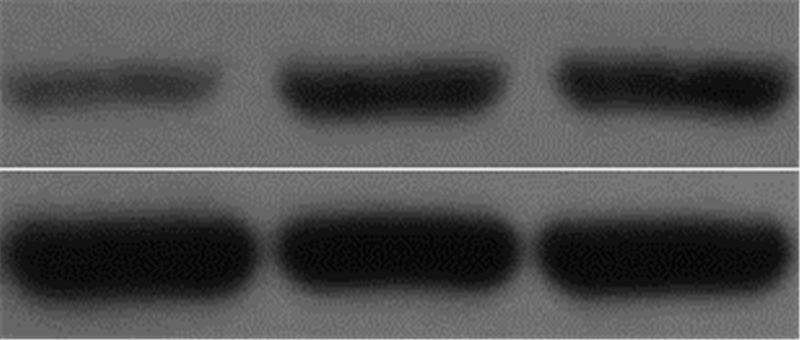 |
| 1:pcDNA3.1;2:pCH9/3091;3:pGEM/HBV1.3图 2 Western blot分析pCH9/3091和pGEM-HBV1.3对cyclin D2表达的影响 |
为了验证cyclin D2沉默对HBV复制的影响,我们用shRNA成功沉默了HepG2.2.15细胞中cyclin D2的表达(图3)。Real-time PCR检测证实shcyclin D2-1和shcyclin D2-2沉默cyclin D2的表达后,单个细胞HBV复制中间体的拷贝数[分别为(60.67±7.09)、(40.67±10.21)]显著低于对照shCont组(95.33±13.5),差异具有统计学意义(P < 0.05)。southern blot检测证实cyclin D2沉默后,HBV复制中间体的表达水平显著降低(图4)。ELISA测定细胞培养上清也发现cyclin D2沉默后,HBsAg和HBeAg分泌明显减少(P < 0.05,图5)。表明cyclin D2沉默显著抑制了HBV的复制和HBV抗原的分泌。
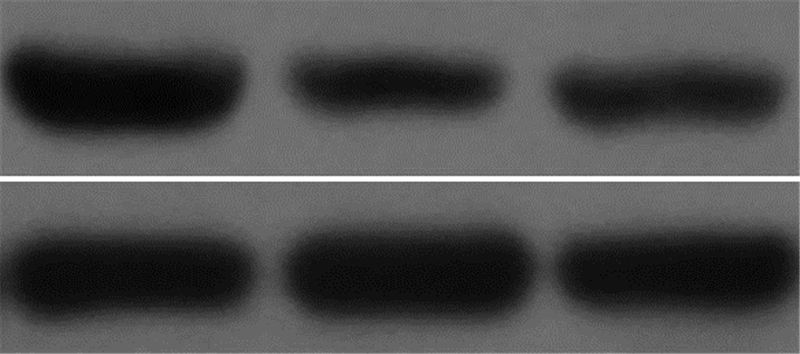 |
| 1:shCont;2:shcyclin D2-1;3:shcyclin D2-2图 3 Western blot验证cyclin D2沉默效果 |
 |
| M:标准;1:shCont;2:shcyclin D2-1;3:shcyclin D2-2图 4 cyclin D2沉默对HBV复制中间体表达的影响 |
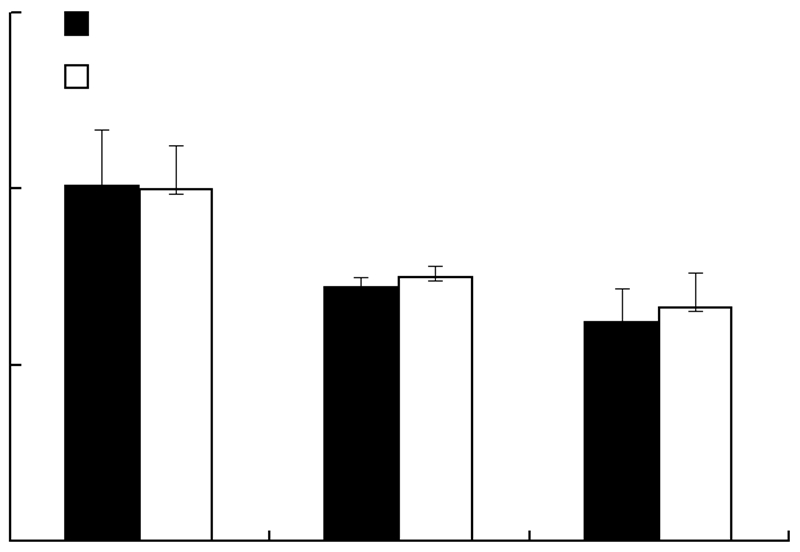 |
| 1:shCont;2:shcyclin D2-1;3:shcyclin D2-2 HBsAg:HBV表面抗原;HBeAg:HBV e抗原 a:P < 0.05 与shCont比较图 5 ELISA检测cyclin D2沉默对HBsAg和HBeAg 分泌的影响 (n=3,x±s) |
另一方面,为了确认cyclin D2对HBV复制的影响,我们在HepG2.2.15细胞中瞬时转染了cyclin D2,Western bot验证cyclin D2过表达是成功的(图6)。Real-time PCR检测分析发现过表达cyclin D2后,单个细胞HBV复制中间体的拷贝数(196.00±19.08)明显高于对照pcDNA3.1组(93.33±5.86)。southern blot分析发现过表达cyclin D2后,HBV复制中间体的表达水平也明显升高(图7)。ELISA测定细胞培养上清也发现过表达cyclin D2组HBsAg表达相对值为(133.33±6.66)明显高于pcDNA3.1组(101.33±11.06),P < 0.05;过表达cyclin D2组HBeAg表达相 对值为(126.00±6.56)明显高于pcDNA3.1组(98.33±10.60),P < 0.05。表明过表达cyclin D2能明显促进HBV的复制和HBV抗原的分泌。
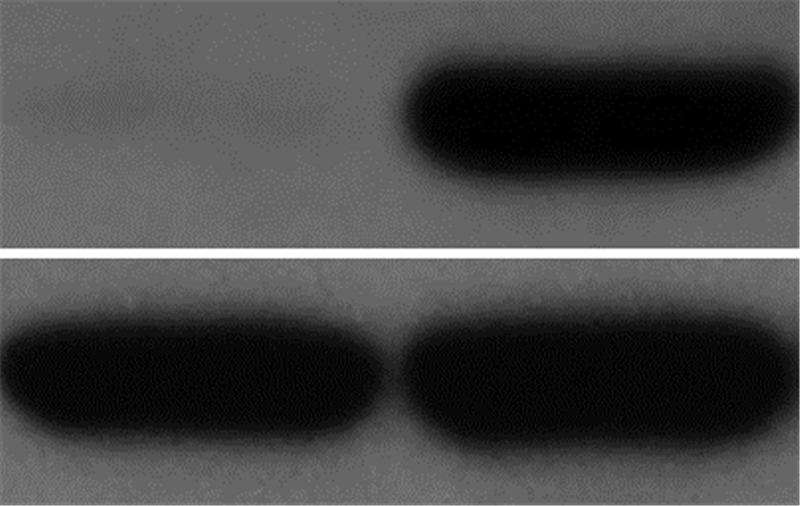 |
| 1:pcDNA3.1;2: cyclin D2图 6 Western blot验证cyclin D2过表达效果 |
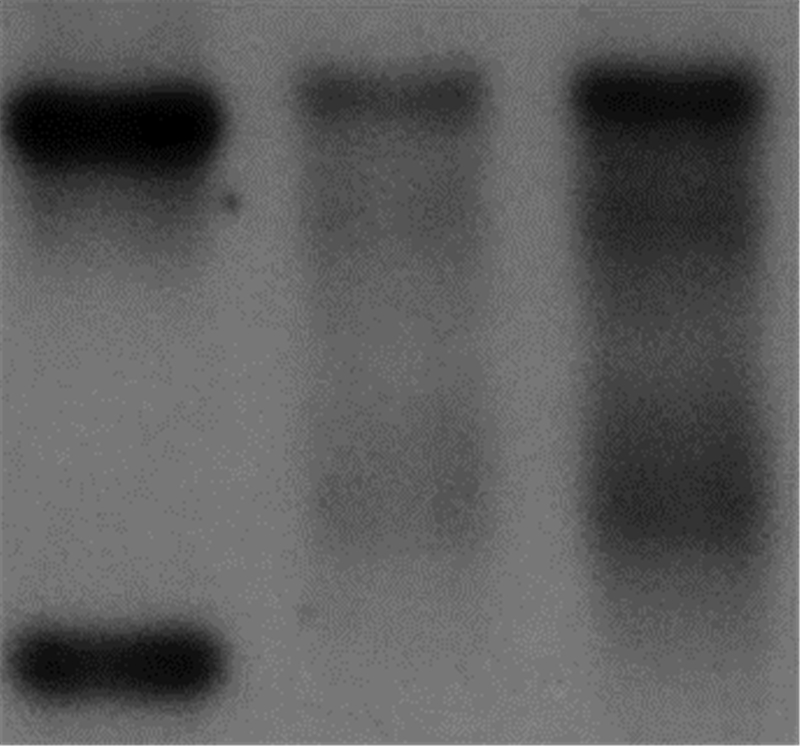 |
| M:标准;1:pcDNA3.1;2: cyclin D2图 7 cyclin D2过表达对HBV复制中间体表达的影响 |
病毒对宿主的感染能力,宿主对病毒的抵抗能力和病毒导致疾病的预后取决于病毒与宿主的相互作用。病毒可通过上调或下调某些宿主因素,从而影响自身的复制。已有研究发现HBV感染可以促进miR146a的转录并下调了STAT1的表达,导致了HBV对干扰素的抵抗[5]。Cyclin D2作为细胞周期蛋白,在调节一些与病毒感染有关的细胞增殖中发挥了关键性的作用。在多种刺激因子作用下,T细胞和B细胞活化时,cyclin D2是第一个被诱导表达的细胞周期蛋白[6, 7, 8],磷脂酰肌醇3-激酶(phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase,PI3K)和环磷腺苷效应元件结合蛋白(cAMP-response element binding protein,CREB)能促进cyclin D2的启动子活性,从而调节了淋巴细胞增殖[9],并且cyclin D2也介导了肿瘤坏死因子家族的B细胞活化因子(B cell-activating factor belonging to the TNF family,BAFF)诱导的CD4+ T淋巴细胞的增殖[10]。近年,有研究报道cyclin D2在HIV病人中的CD4+ T细胞中表达减少[11],cyclin D2 mRNA水平在人呼吸道合胞病毒感染的气道上皮细胞中的表达水平也降低[12]。这些发现说明cyclin D2是病毒感染重要的宿主因素之一。
Park等[13]发现cyclin D2的多态性与HBV感染的清除有关,揭示着cyclin D2可能参与了HBV的生活周期。本课题组也研究发现cyclin D2与HBV复制密切相关,在细胞周期蛋白家族中,cyclin D2在HBV复制细胞与对照细胞中的表达差异最为显著,瞬时感染HBV后,cyclin D2的mRNA和蛋白水平都显著上升。进一步研究发现cyclin D2能明显促进HBV复制中间体的表达和病毒抗原的分泌。
Cyclin D2除了具有调节细胞周期的作用外,还是多条信号通路中重要的信号分子。人类T细胞白血病病毒Ⅰ型(human T-lymphotropic virus 1,HTLV-1)的转录活化蛋白(Tax)可通过NFκB诱导cyclin D2活化[14],Cyclin D2也是BCR-ABL/FoxO3a信号通路重要的下游靶点[15],Myc-cyclin D2-p27信号通路也在休眠细胞的周期进展中发挥了重要作用[16]。HBV的转录需要多种信号分子的参与,研究报道某些转录因子可结合于HBV核心启动子上参与了HBV复制的调控,如:Sp1[17]、PPAR-alpha[18]、AP1[19]、HNF4[20]、NFκB[21]等。本课题组下一步将通过研究cyclin D2对信号通路的影响,进一步阐明cyclin D2上调HBV复制的分子机制,从而为发展控制HBV感染的治疗策略提供新的靶点。
| [1] | Kato J Y, Sherr C J. Inhibition of granulocyte differentiation by G1 cyclins D2 and D3 but not Dl[J]. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 1993, 90(24): 11513-11517. |
| [2] | Song H, Hogdall E, Ramus S J, et al. Effects of common germ-line genetic variation in cell cycle genes on ovarian cancer survival[J]. Clin Cancer Res, 2008, 14(4): 1090-1095. |
| [3] | Wang Y, Cheng J, Xu C, et al. Quantitative methylation analysis reveals gender and age differences in p16INK4a hypermethylation in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. Liver Int, 2012, 32(3): 420-428. |
| [4] | Choi Y L, Park S H, Jang J J, et al. Expression of the G1-S modulators in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma and dysplastic nodule: association of cyclin D1 and p53 proteins with the progression of hepatocellular carcinoma[J]. J Korean Med Sci, 2001, 16(4): 424-432. |
| [5] | Hou Z H, Han Q J, Zhang C, et al. miR146a impairs the IFN-induced anti-HBV immune response by downregulating STAT1 in hepatocytes[J]. Liver Int, 2014, 34(1): 58-68. |
| [6] | Appleman L J, Berezovskaya A, Grass I, et al. CD28 costimulation mediates T cell expansion via IL-2-independent and IL-2-dependent regulation of cell cycle progression[J]. J Immunol, 2000, 164(1): 144-151. |
| [7] | Lam E W, Glassford J, Banerji L, et al. Cyclin D3 compensates for loss of cyclin D2 in mouse B-lymphocytes activated via the antigen receptor and CD40[J]. J Biol Chem, 2000, 275(5): 3479-3484. |
| [8] | Martino A, Holmes J H 4th, Lord J D, et al. Stat5 and Sp1 regulate transcription of the cyclin D2 gene in response to IL-2[J]. J Immunol, 2001, 166(3): 1723-1729. |
| [9] | White P C, Shore A M, Clement M, et al. Regulation of cyclin D2 and the cyclin D2 promoter by protein kinase A and CREB in lymphocytes[J]. Oncogene, 2006, 25(15): 2170-2180. |
| [10] | Ji F, Chen R, Liu B, et al. BAFF induces spleen CD4+ T cell proliferation by down-regulating phosphorylation of FOXO3A and activates cyclin D2 and D3 expression[J]. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2012, 425(4): 854-858. |
| [11] | Sieg S F, Harding C V, Lederman M M. HIV-1 infection impairs cell cycle progression of CD4(+) T cells without affecting early activation responses[J]. J Clin Invest, 2001, 108(5): 757-764. |
| [12] | Wu W, Munday D C, Howell G, et al. Characterization of the interaction between human respiratory syncytial virus and the cell cycle in continuous cell culture and primary human airway epithelial cells[J]. J Virol, 2011, 85(19): 10300-10309. |
| [13] | Park T J, Chun J Y, Bae J S, et al. CCND2 polymorphisms associated with clearance of HBV Infection[J]. J Hum Genet, 2010, 55(7): 416-420. |
| [14] | Iwanaga R, Ozono E, Fujisawa J, et al. Activation of the cyclin D2 and cdk6 genes through NF-kappaB is critical for cell-cycle progression induced by HTLV-I Tax[J]. Oncogene, 2008, 27(42): 5635 5642. |
| [15] | Fernandez-de-Mattos S, Essafi A, Soeiro I, et al. Soeiro I, FoxO3a and BCR-ABL regulate cyclin D2 transcription through a STAT5/BCL6-dependent mechanism[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2004, 24(22): 10058 10071. |
| [16] | Bouchard C, Thieke K, Maier A, et al. Direct induction of cyclin D2 by Myc contributes to cell cycle progression and sequestration of p27[J]. EMBO J, 1999, 18(19): 5321-5333. |
| [17] | Li J, Ou J H. Differential regulation of hepatitis B virus gene expression by the Sp1 transcription factor[J]. J Virol, 2001, 75(18): 8400-8406. |
| [18] | Tseng Y P, Kuo Y H, Hu C P, et al. The role of helioxanthin in inhibiting human hepatitis B viral replication and gene expression by interfering with the host transcriptional machinery of viral promoters[J]. Antiviral Res, 2008, 77(3): 206-214. |
| [19] | Ren J H, Tao Y, Zhang Z Z, et al. Sirtuin 1 regulates hepatitis B virus transcription and replication by targeting transcription factor AP-1[J]. J Virol, 2014, 88(5): 2442-2451. |
| [20] | Zheng Y, Li J, Ou J H. Regulation of hepatitis B virus core promoter by transcription factors HNF1 and HNF4 and the viral X protein[J]. J Virol, 2004, 78(13): 6908-6914. |
| [21] | Kwon J A, Rho H M. Hepatitis B viral core protein activates the hepatitis B viral enhancer II/pregenomic promoter through the nuclear factor kappaB binding site[J]. Biochem Cell Biol, 2002, 80(4): 445-455. |



