血管平滑肌细胞(vascular smooth muscle cell,VSMC)表型转换是由分化的静止收缩表型转换为去分化的合成分泌表型,从而导致VSMC增殖、迁移能力增强[1]。研究证实,胰岛素干预培养的VSMC后,VSMC发生了表型转换,其增殖及迁移能力明显增强[2],并且决定VSMC分化的静止收缩型的标志蛋白α肌动蛋白(alpha smooth muscle actin,SM-α)显著下调[3],最终促使VSMC生物学功能异常,该过程在人类和大鼠均可观察到[4]。
激活蛋白-1(activator protein 1,AP-1)是细胞内的一个转录因子,由c-Jun和c-Fos蛋白家族组成的异二聚体[5]。在不同的组织细胞,激活的AP-1能结合特定的基因序列,控制着分化、凋亡等细胞进程。在VSMC中,AP-1能结合于SM-α启动子特异区域的一段序列,从而进一步引起下游的反应[6]。但是,在胰岛素诱导VSMC表型转换中,SM-α基因表达下调是否与AP-1有关尚不清楚,胰岛素促进VSMC表型转换是否是通过AP-1调控SM-α基因表达下调来实现有待探究。因此,本实验通过胰岛素、AP-1表达载体及胰岛素+AP-1表达载体干扰大鼠VSMC,探讨胰岛素诱导VSMC表型转换标志基因SM-α表达下调与转录因子AP-1之间的关系。 1 材料与方法 1.1 质粒、细胞和主要试剂
SM-α启动子特异区域转录因子AP-1结合位点的序列参照http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/NM_007392.3。AP-1表达载体质粒购于广州复能基因有限公司;质粒转化宿主菌大肠杆菌XL1-Blue由第三军医大学基础医学部医学遗传学教研室章波教授惠赠;SD大鼠VSMC株购自美国ATCC。Real-time PCR试剂盒购自TaKaRa公司;质粒提取试剂盒购自Omega公司;Lipofectamine 2000转染试剂购自上海联硕公司;DMEM细胞培养基和胰酶消化液均购自赛默飞世尔公司;胎牛血清购自成都哈里生物公司;AP-1鼠单克隆抗体购自密理博公司;SM-α鼠单克隆抗体和辣根酶标记山羊抗兔IgG二抗均购自中杉金桥生物技术有限公司;AP-1基因及SM-α启动子区特异序列引物合成为上海生工生物工程有限公司。 1.2 转染及分组
将对数生长期的VSMC按每孔2×105个分4组接种于6孔板上:空白对照组、胰岛素干扰组、AP-1表达载体组、胰岛素+AP-1表达载体组(n=3)。将接种好的培养板放置37 ℃、5% CO2培养箱中培养24 h后,参照说明书用Lipofectamine 2000转染试剂转染,24 h后在荧光显微镜下观察。 1.3 流式细胞仪检测细胞周期
分别收集空白对照组与不同浓度(25、50、100、125 nmol/L)胰岛素干扰组的细胞(n=3),PBS洗涤,70%乙醇4 ℃固定过夜,离心后弃上清,PBS洗涤,加100 μL RNase于37 ℃水浴30 min,加入500 μL碘化丙啶(50 μg/mL)染液4 ℃避光30 min,上机检测。 1.4 Western blot检测AP-1及SM-α蛋白表达
收集以上分组的细胞,加入80 μL预冷的细胞裂解液,超声破碎仪破碎提取各组总蛋白,测定浓度后常规进行SDS-PAGE电泳。95 V电泳120 min,15 V电转入DVPF膜约50 min,封闭液4 ℃封闭2 h,分别加入兔抗大鼠AP-1(1 ∶2 000),兔抗大鼠SM-α(1 ∶2 000),4℃孵育过夜,PBST漂洗3次后加入辣根酶标记山羊抗兔IgG(1 ∶2 000),室温孵育1 h,PBST漂洗3次后ECL显影液显色,Bio-Rad凝胶成像系统扫描成像。以磷酸甘油醛脱氢酶(GAPDH)为内参参照,用Quantity One软件分析条带灰度值。 1.5 RT-PCR检测AP-1及SM-α的mRNA表达
提取以上分组细胞的总RNA,按TaKaRa试剂盒将RNA逆转录成cDNA。在Bio-Rad PCR上进行定量PCR反应,其反应总体系包括:2×SYBR Premix Ex TaqTMⅡ,去离子水,PCR上游引物,PCR下游引物,模板为cDNA。反应条件为:95 ℃预变性5 min;95 ℃ 10 s,58 ℃ 20 s,72 ℃ 30 s,共45个循环。AP-1上游引物:5′-CTCAGCAACTTCAACCCG-3′,下游引物:5′-GCACTTGGAGGCAGCGAT-3′,扩增片段为260 bp;SM-α 上游引物:5′- CGGGCATCCACGAAACCA-3′,下游引物:5′-CCGCCGATCCAGACAGAA-3′,扩增片段为200 bp,内参GAPDH上游引物:5′-TCTGCTCCTCCCTGTTC-3′,下游引物:5′-CACCCCATTTGATGTTAG-3′,扩增片段为327 bp。 1.6 统计学分析
计量资料用 x±s表示,采用SPSS 17.0统计软件对实验数据进行单因素方差分析。 2 结果 2.1 胰岛素对VSMC细胞周期的影响
如图 1所示,不同浓度的胰岛素体外处理大鼠VSMC 24 h后,处于S期的细胞百分比呈现先上升后下降的趋势。该结果显示,胰岛素作用于VSMC,使S期的比例增加,引起VSMC发生表型转换,进而导致VSMC增殖,差异有统计学意义(P<0.05),在100 nmol/L 的浓度下,发挥的效应最佳,因此,我们选择100 nmol/L的胰岛素浓度进行后续的实验。
 |
| A:空白对照组;B:25 nmol/L胰岛素组;C:50 nmol/L胰岛素组;D:100 nmol/L胰岛素组;E:125 nmol/L胰岛素组;F:各组S期百分比(n=3) 图 1 各组VSMC细胞周期流式细胞仪检测结果与定量分析结果 |
与空白对照组比较,胰岛素组中AP-1、SM-α的mRNA水平同时下降(P<0.05),AP-1表达载体组中AP-1、SM-α的mRNA水平同时升高(P<0.05),而胰岛素+AP-1表达载体组中AP-1、SM-α的mRNA水平无明显变化(P>0.05,图 2)。
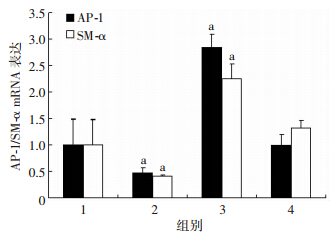 |
| 1:空白对照组;2:胰岛素组干扰组;3:AP-1表达载体组;4:胰岛素+AP-1表达载体组 a:P<0.05,与空白对照组比较 图 2 RT-PCR检测胰岛素诱导VSMC的AP-1、SM-α mRNA表达 |
AP-1蛋白表达水平:与空白对照组比较,胰岛素+AP-1表达载体组无明显变化(P>0.05),胰岛素干扰组明显下降(P<0.01),而AP-1表达载体组明显升高(P<0.01)。SM-α蛋白表达水平:与空白对照组比较,胰岛素+AP-1表达载体组无明显变化(P>0.05),胰岛素干扰组明显下降(P<0.01),而AP-1表达载体组明显升高(P<0.01,图 3)。AP-1蛋白表达水平与SM-α蛋白表达水平的变化趋势相一致。
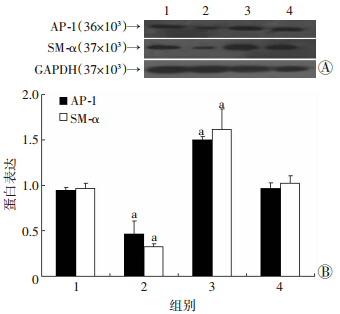 |
| 1:空白对照组;2:胰岛素干扰组;3:AP-1表达载体组;4:胰岛素+AP-1表达载体组 A:Western blot检测结果;B:半定量分析结果 a:P<0.01,与空白对照组比较 图 3 Western blot检测胰岛素诱导VSMC的AP-1、SM-α 蛋白表达水平 |
临床资料显示,患病多年的2型糖尿病患者长时间地应用高剂量胰岛素后,其合并大血管动脉粥样硬化的概率明显增高[7, 8],可能与VSMC由分化的静止收缩表型转换为去分化的合成分泌表型[9]。本研究通过不同浓度的胰岛素刺激VSMC体外培养24 h后,采用流式细胞术检测其细胞周期,发现S期百分比呈浓度依赖性的升高,并且在100 nmol/L的浓度下达到峰值后开始小幅度的下降。因此,我们推测胰岛素作用于VSMC的S期,引起VSMC发生表型转换,进而导致VSMC增殖。
SM-α是VSMC细胞骨架的结构蛋白,其在细胞运动及收缩中起了关键性的作用[10]。当血流发生异常、血胆固醇升高、血管内皮损伤等因素引起血管壁斑块形成时,观察到VSMC中SM-α的表达大大降低[11]。Kee等[12]发现SM-α基因是分化静止收缩表型的VSMC中高表达的基因标记之一,当分化的静止收缩表型的VSMC向去分化的合成分泌表型转换时,细胞中SM-α的量大大降低。Crawford等[13]发现,缺少SM-α的鼠由于VSMC生长及功能异常,在出生后不久就死亡了。AP-1是细胞内的一个转录激活因子。通过特定的保守序列与一定的受体和一些信号通路蛋白的基因结合来启动基因的表达,从而控制了许多细胞进程,包括分化、凋亡等[14]。有研究发现,VSMC中AP-1能维持其分化的静止收缩表型[15]。并发现AP-1在静止收缩表型的VSMC中表达升高且其引导的与维持VSMC静止收缩型相关的下游信号通路表现活跃[16]。因而推测:胰岛素诱导VSMC表型转换决定基因SM-α下调与转录因子AP-1可能存在相关性。实验证实,上调VSMC中AP-1表达,VSMC表型决定基因SM-α表达上调,胰岛素可以抑制AP-1上调SM-α的表达水平。
本实验结果提示:胰岛素诱导VSMC表型转换决定基因SM-α下调与转录因子AP-1的表达下调相关,最终引起了VSMC的表型转换导致其发生增殖,为胰岛素诱导VSMC表型转换的内在机制深入研究提供了新的研究靶点。本研究仅观察胰岛素诱导增殖时SM-α 表达下调的现象是否与该基因启动子区转录因子AP-1 相关,其机制有待深入研究。
| [1] | Zhang J, Zheng B, Zhou P P, et al. Vascular calcification is coupled with phenotypic conversion of vascular smooth muscle cells through KLF5-mediated transactivation of the Runx2 promoter[J].Biosci Rep, 2014, [Epub ahead of print]. |
| [2] | Cersosimo E, Xu X, Upala S, et al. Acute insulin resistance stimulates and insulin sensitization attenuates vascular smooth muscle cell migration and proliferation[J].Physiol Rep, 2014, 2(8): e12123. |
| [3] | Bhattacharyya A, Lin S, Sandig M, et al. Regulation of vascular smooth muscle cell phenotype in three-dimensional coculture system by Jagged1-selective Notch3 signaling[J]. Tissue Eng Part A, 2014, 20(7/8): 1175-1187. |
| [4] | Wang C C, Gurevich I, Draznin B. Insulin affects vascular smooth cell phenotype and migration via distinct signaling pathways[J]. Diabetes, 2003, 52(10): 2562-2569. |
| [5] | Milde-Langosch K. The Fos family of transcription factors and their role in tumourigenesis[J]. Eur J Cancer, 2005, 41(16): 2449-2461. |
| [6] | Zhang H W, Zhang T, Shen B Z, et al. Toxicological insight from AP-1 silencing study on proliferation, migration, and dedifferentiation of rat vascular smooth muscle cell[J]. Cardiovasc Toxicol, 2012, 12(1): 25- 38. |
| [7] | Sun X, Han F, Yi J, et al. The effect of telomerase activity on vascular smooth muscle cell proliferation in type 2 diabetes in vivo and in vitro[J]. Mol Med Rep, 2013, 7(5): 1636-1640. |
| [8] | 王旭开, 杨成明, 王红勇, 等. 医源性不同胰岛素剂量对中年2型糖尿病患者合并冠状动脉事件的作用[J]. 中国动脉硬化杂志, 2005, 13(3): 345-347. |
| [9] | Allahverdian S, Chehroudi A C, Mcmanus B M, et al. Contribution of intimal smooth muscle cells to cholesterol accumulation and macrophage-like cells in human atherosclerosis[J].Circulation, 2014, 129(15): 1551-1559. |
| [10] | Weymouth N, Shi Z, Rockey D C. Smooth muscle α actin is specifically required for the maintenance of lactation[J]. Dev Biol, 2012, 363(1): 1-14. |
| [11] | Chen C H, Ho H H, Wu M L, et al. Modulation of cysteine-rich protein 2 expression in vascular injury and atherosclerosis[J]. Mol Biol Rep, 2014, 41(11): 7033-7041. |
| [12] | Kee H J, Kim G R, Cho S N, et al. miR-18a-5p MicroRNA Increases Vascular Smooth Muscle Cell Differentiation by Downregulating Syndecan4[J]. Korean Circ J, 2014, 44(4): 255-263. |
| [13] | Crawford K, Flick R, Close L, et al. Mice lacking skeletal muscle actin show reduced muscle strength and growth deficits and die during the neonatal period[J]. Mol Cell Biol, 2002, 22(16): 5887-5896. |
| [14] | Lazenka M F, David B G, Lichtman A H, et al. Delta FosB and AP-1-mediated transcription modulate cannabinoid CB1 receptor signaling and desensitization in striatal and limbic brain regions[J]. Biochem Pharmacol, 2014, 91(3): 380-389. |
| [15] | Zhao J, Imbrie G A, Baur W E, et al. Estrogen receptor-mediated regulation of microRNA inhibits proliferation of vascular smooth muscle cells[J]. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol, 2013, 33(2): 257-265. |
| [16] | Guo Y, Fan Y, Zhang J, et al. Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ coactivator 1β (PGC-1β) protein attenuates vascular lesion formation by inhibition of chromatin loading of minichromosome maintenance complex in smooth muscle cells[J]. J Biol Chem, 2013, 288(7): 4625-4636. |



